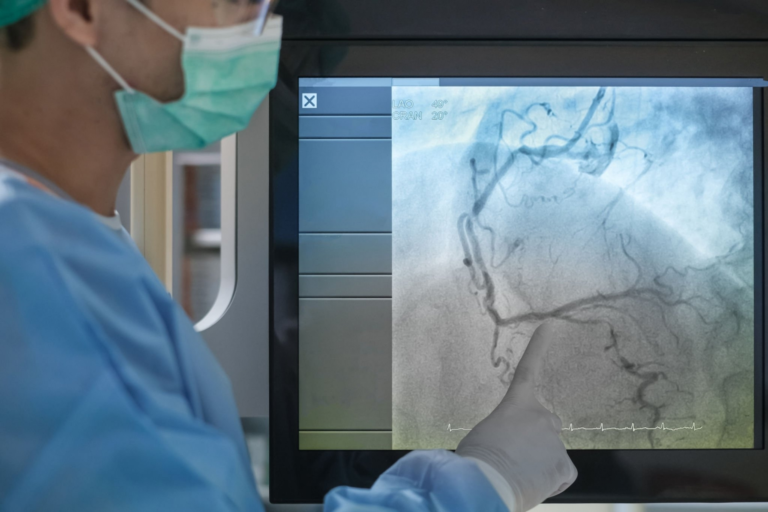
What is Angiography?
Angiography is an imaging technique used to view the blood vessels and organs of the body. It uses a contrast dye and X-ray images to produce detailed pictures of the organs and vessels, including their size and shape. The procedure is used to diagnose and treat a variety of vascular conditions, such as blockages, aneurysms, and stenosis.
Benefits of Angiography
Angiography provides an accurate view of the body’s vascular system, allowing doctors to diagnose and treat conditions more accurately. This can help to reduce complications from misdiagnosis or delays in treatment. Additionally, angiography can be used to plan a procedure, such as surgery, and to monitor the progress of a treatment.

Preparation for Angiography
Prior to the procedure, it is important to inform the doctor of any allergies, medications, and medical conditions. The doctor may also ask the patient to fast for a period of time before the procedure.
Angiography Procedure
During the procedure, a thin tube called a catheter is inserted into an artery. The catheter is then used to inject a contrast dye into the blood vessels. This dye allows the doctor to view the vessels and organs on the X-ray images. The procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia.
Recovery from Angiography
Most people can return to their normal activities within a day or two of the procedure. However, it is important to follow the doctors’ instructions, including taking any medications and avoiding strenuous activities.
Conclusion
Angiography is a safe and effective imaging technique used to diagnose and treat a variety of vascular conditions. It is important to follow the doctors’ instructions before and after the procedure to reduce the risk of complications
